The syntax to place an IP address on the interface is:
ip address ip-address mask
Given the routers below, we wish to configure IP addresses on Router1 and Router2
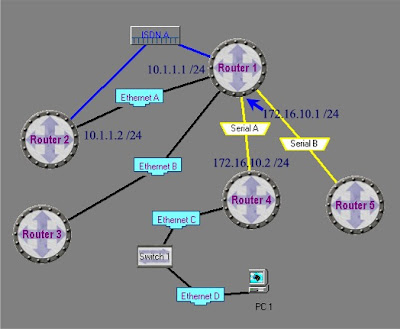
Remember the the /24 means 255.255.255.0. For your convenience here is a handy table:
Slash Dotted Decimal Slash Dotted Decimal Slash Dotted Decimal
/8 255.0.0.0 /16 255.255.0.0 /24 255.255.255.0
/9 255.128.0.0 /17 255.255.128.0 /25 255.255.255.128
/10 255.192.0.0 /18 255.255.192.0 /26 255.255.255.192
/11 255.224.0.0 /19 255.255.224.0 /27 255.255.255.224
/12 255.240.0.0 /20 255.255.240.0 /28 255.255.255.240
/13 255.248.0.0 /21 255.255.248.0 /29 255.255.255.248
/14 255.252.0.0 /22 255.255.252.0 /30 255.255.255.252
/15 255.254.0.0 /23 255.255.254.0 /31 255.255.255.254
Let's start configuring Router 1
Router>
Router>en
Router#conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int e0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#int s0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#end%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#
We can view the IP addresses on the interface:
Router#sh ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
BRI0 unassigned YES manual admin down down
Ethernet0 10.1.1.1 YES manual admin down down
Ethernet0 10.1.2.2 YES manual admin down down
Router#
We have assigned an IP address to each interface but the interface is still administratively down because we have not executed a 'no shutdown' command on each interface.
Now you should go to each of the interfaces and type no shutdown, this should turn the interfaces to up.
Connect to Router 2 We would also like to add ip addresses to the interfaces.
Router>
Router>en
Router#conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int e0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#int s0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#exit%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router(config)#exit
Router#exit
PING
PING, the Packet Inter Net Groper, allows a user to test basic connectivity. The syntax is:
ping ip-address
The router will send out five echo requests to the destination IP address, if it receives a reply, it will not it with an '!', if not reply is received it will note it with a '.'.
A successful ping:
Router#ping 10.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/37/44 ms
Router#
A failed ping:
Router#ping 2.2.2.2
Type escape sequence to abort.Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Router#
Ping is one of the most commonly used test tools in the word. PING uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to communicate with other routers.
You can also view your ip addresses using the command show running-config or show ip interface.
Copyright (c) 2001 Boson Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved
No comments:
Post a Comment